安装 nginx
下载 nginx 的压缩包文件到根目录,官网下载地址:nginx.org/download/nginx-x.xx.xx.tar.gz
yum update #更新系统软件
cd /
wget nginx.org/download/nginx-1.17.2.tar.gz
解压 tar.gz 压缩包文件,进去 nginx-1.17.2
tar -xzvf nginx-1.17.2.tar.gz
cd nginx-1.17.2
进入文件夹后进行配置检查
./configure
通过安装前的配置检查,发现有报错。检查中发现一些依赖库没有找到,这时候需要先安装 nginx 的一些依赖库
yum -y install pcre* #安装使nginx支持rewrite
yum -y install gcc-c++
yum -y install zlib*
yum -y install openssl openssl-devel
再次进行检查操作
./configure
没发现报错显示,接下来进行编译并安装的操作
// 检查模块支持
./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx --with-http_ssl_module --with-http_v2_module --with-http_realip_module --with-http_addition_module --with-http_sub_module --with-http_dav_module --with-http_flv_module --with-http_mp4_module --with-http_gunzip_module --with-http_gzip_static_module --with-http_auth_request_module --with-http_random_index_module --with-http_secure_link_module --with-http_degradation_module --with-http_slice_module --with-http_stub_status_module --with-mail --with-mail_ssl_module --with-stream --with-stream_ssl_module --with-stream_realip_module --with-stream_ssl_preread_module --with-threads --user=www --group=www
这里得特别注意下,你以后需要用到的功能模块是否存在,不然以后添加新的包会比较麻烦。
编译并安装
make && make install
这里需要注意,模块的支持跟后续的 nginx 配置有关,比如 SSL,gzip 压缩等等,编译安装前最好检查需要配置的模块存不存在。
查看 nginx 安装后在的目录,可以看到已经安装到 /usr/local/nginx 目录了
查看默认安装的模块支持
查看 nginx 的文件列表,可以发现里面有一个 auto 的目录。在这个 auto 目录中有一个 options 文件,这个文件里面保存的就是 nginx 编译过程中的所有选项配置。
通过命令:
cat nginx-1.17.2/auto/options | grep YES
nginx 配置
内置变量
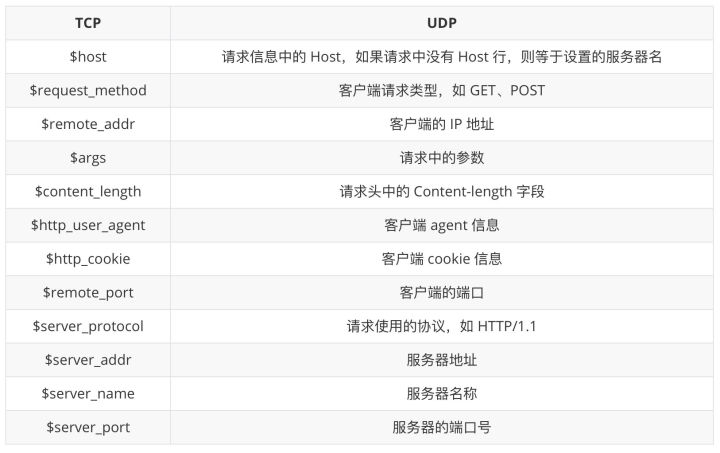
基本结构
main # 全局配置,对全局生效
├── events # 配置影响 nginx 服务器或与用户的网络连接
├── http # 配置代理,缓存,日志定义等绝大多数功能和第三方模块的配置
│ ├── upstream # 配置后端服务器具体地址,负载均衡配置不可或缺的部分
│ ├── server # 配置虚拟主机的相关参数,一个 http 块中可以有多个 server 块
│ ├── server
│ │ ├── location # server 块可以包含多个 location 块,location 指令用于匹配 uri
│ │ ├── location
│ │ └── ...
│ └── ...
└── ...
主要配置含义
- main:nginx 的全局配置,对全局生效。
- events:配置影响 nginx 服务器或与用户的网络连接。
- http:可以嵌套多个 server,配置代理,缓存,日志定义等绝大多数功能和第三方模块的配置。
- server:配置虚拟主机的相关参数,一个 http 中可以有多个 server。
- location:配置请求的路由,以及各种页面的处理情况。
- upstream:配置后端服务器具体地址,负载均衡配置不可或缺的部分。
nginx.conf 配置文件的语法规则
- 配置文件由指令与指令块构成
- 每条指令以 “;” 分号结尾,指令与参数间以空格符号分隔
- 指令块以 {} 大括号将多条指令组织在一起
- include 语句允许组合多个配置文件以提升可维护性
- 通过 # 符号添加注释,提高可读性
- 通过 $ 符号使用变量
- 部分指令的参数支持正则表达式,例如常用的 location 指令
常用命令
nginx -s reload # 向主进程发送信号,重新加载配置文件,热重启
nginx -s reopen # 重启 Nginx
nginx -s stop # 快速关闭
nginx -s quit # 等待工作进程处理完成后关闭
nginx -T # 查看当前 Nginx 最终的配置
nginx -t -c <配置路径> # 检查配置是否有问题,如果已经在配置目录,则不需要 -c
配置 nginx 开机自启
利用 systemctl 命令
如果用 yum install 命令安装的 nginx,yum 命令会自动创建 nginx.service 文件,直接用命令:
systemctl enable nginx # 设置开机启动 Nginx
systemctl disable nginx # 关闭开机启动 Nginx
就可以设置开机自启,否则需要在系统服务目录里创建 nginx.service 文件。
创建并打开 nginx.service 文件:
vi /lib/systemd/system/nginx.service
内容如下:
[Unit]
Description=nginx
After=network.target
[Service]
Type=forking
ExecStart=/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
ExecReload=/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s reload
ExecStop=/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s quit
PrivateTmp=true
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
加载服务
systemctl daemon-reload
nginx 常用功能
正向代理
通过 Nginx 的正向代理审计监控内网用户的外网访问记录
一个位于客户端和目标服务器之间的 Nginx 正向代理服务器, 客户端向 Nginx 正向代理发送一个请求并指定目标服务器,然后代理向目标服务器转交请求并将获得的内容返回给客户端及本地代理服务器缓存
适用场景:
- 用于解决内网服务器通过代理服务器访问外网
- 监控内网终端的外网访问记录
- 代理端缓存外网访问的响应结构,加速外网访问
正向代理又细分为 http、https 流量的透明代理和非透明代理
- 透明代理指利用内网 dns 将待访问的域名解析到 Nginx 的透明代理, 终端用户利用内网 dns 后不需要进行任何代理服务器设置
- 非透明代理指终端用户需要设置代理服务器信息
如何代理加密的 HTTPS 流量是正向代理需要解决的主要问题, 当前主要的两种方式:
- 七层解决:HTTP CONNECT 透传(隧道)模式, 即不解密不感知上层流量
- 四层解决: NGINX Stream
http 流量
1、透明代理, 利用本机 hosts 或 DNS 解析待访问的目标域名到代理服务器 Ip
# Nginx 透明正向代理 http 流量主要配置
server {
resolver 114.114.114.114;
listen 80;
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.80.log main;
location / {
proxy_pass http://$http_host$request_uri;
proxy_set_header HOST $http_host;
proxy_buffers 256 4k;
proxy_max_temp_file_size 0k;
proxy_connect_timeout 30;
proxy_send_timeout 60;
proxy_read_timeout 60;
proxy_next_upstream error timeout invalid_header http_502;
}
}
2、非透明代理, 需在客户终端设置代理服务器信息
# Nginx 非透明正向代理 http 流量主要配置
server {
resolver 114.114.114.114;
listen 1080;
location / {
proxy_pass http://$http_host$request_uri;
proxy_set_header HOST $http_host;
proxy_buffers 256 4k;
proxy_max_temp_file_size 0k;
proxy_connect_timeout 30;
proxy_send_timeout 60;
proxy_read_timeout 60;
proxy_next_upstream error timeout invalid_header http_502;
}
}
https 流量
1、HTTP CONNECT 隧道 方式(非透明代理)
# 需要 ngx_http_proxy_connect_module 模块支持; 客户端需要指定 https 代理服务器
yum -y install gcc-c++ zlib-devel openssl-devel.x86_64 pcre-devel gd-devel patch
wget http://nginx.org/download/nginx-1.20.1.tar.gz
tar xf nginx-1.20.1.tar.gz && cd nginx-1.20.1
# 给 nginx 打补丁, 需要根据不同的 nginx 版本 选择对应的补丁
cd /root/src/ && git clone https://github.com/chobits/ngx_http_proxy_connect_module
cd nginx-1.20.1
patch -p1 < /root/src/ngx_http_proxy_connect_module/patch/proxy_connect_rewrite_1018.patch
./configure --prefix=/etc/nginx --sbin-path=/usr/sbin/nginx --modules-path=/usr/lib64/nginx/modules --conf-path=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf --error-log-path=/var/log/nginx/error.log --http-log-path=/var/log/nginx/access.log --pid-path=/var/run/nginx.pid --lock-path=/var/run/nginx.lock --http-client-body-temp-path=/var/cache/nginx/client_temp --http-proxy-temp-path=/var/cache/nginx/proxy_temp --http-fastcgi-temp-path=/var/cache/nginx/fastcgi_temp --http-uwsgi-temp-path=/var/cache/nginx/uwsgi_temp --http-scgi-temp-path=/var/cache/nginx/scgi_temp --user=nginx --group=nginx --with-compat --with-file-aio --with-threads --with-http_addition_module --with-http_auth_request_module --with-http_dav_module --with-http_flv_module --with-http_gunzip_module --with-http_gzip_static_module --with-http_mp4_module --with-http_random_index_module --with-http_realip_module --with-http_secure_link_module --with-http_slice_module --with-http_ssl_module --with-http_stub_status_module --with-http_sub_module --with-http_v2_module --with-mail --with-mail_ssl_module --with-stream --with-stream_realip_module --with-stream_ssl_module --with-stream_ssl_preread_module --with-cc-opt='-O2 -g -pipe -Wall -Wp,-D_FORTIFY_SOURCE=2 -fexceptions -fstack-protector-strong --param=ssp-buffer-size=4 -grecord-gcc-switches -m64 -mtune=generic -fPIC' --with-ld-opt='-Wl,-z,relro -Wl,-z,now -pie' \
--add-module=/root/src/ngx_http_proxy_connect_module
make && make install
mkdir -p /var/cache/nginx/client_temp && useradd -M -r -s /sbin/nologin nginx
# nginx server 配置
server {
listen 8443;
resolver 114.114.114.114;
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.8443.log main;
proxy_connect;
proxy_connect_allow 443;
proxy_connect_connect_timeout 10s;
proxy_connect_read_timeout 10s;
proxy_connect_send_timeout 10s;
location / {
proxy_pass http://$host;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
}
}
# linux 命令行设置 http 代理服务器
export http_proxy="192.168.31.68:1080"
export http_proxy="192.168.31.68:8443"
# 通过 curl 测试代理服务器是否正常
curl --proxy 192.168.31.68:8443 https://www.baidu.com -svo /dev/null
curl http://192.168.31.17:1083 -svo /dev/null
2、NGINX Stream 方式(HTTPS 流量的透明正向代理)
- 需要 --with-stream,--with-stream_ssl_preread_module、--with-stream_ssl_module 模块的支持;
- 利用 ngx_stream_ssl_preread_module 模块, 在不解密的情况下拿到 HTTPS 流量待访问目标域名(利用 TLS/SSL 握手的第一个 Client Hello 报文中的扩展地址 SNI (Server Name Indication)来获取);
- 如果客户端没有携带 SNI 字段,会造成代理服务器无法获取待访问目标服务域名,导致访问不成功; 因此要求所有客户端都需要在 TLS/SSL 握手中带上 SNI 字段!!
- 将待访问的所有域名利用内网 dns 或 hosts 解析到代理服务器; 客户端侧则不需要指定代理服务器信息
stream {
resolver 114.114.114.114;
log_format main '$remote_addr - [$time_local] '
'$protocol $status $bytes_sent $bytes_received $session_time "$upstream_addr" '
'"$upstream_bytes_sent" "$upstream_bytes_received" "$upstream_connect_time" '
'$remote_addr $remote_port $server_addr $server_port';
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.443.log main;
server {
listen 443;
ssl_preread on;
proxy_connect_timeout 5s;
proxy_pass $ssl_preread_server_name:$server_port;
}
}
# 命令行测试 或 通过浏览器测试
# 将要访问的目标域名通过本机 hosts 或 内网 dns 解析到代理服务器
openssl s_client -connect www.baidu.com:443 -servername www.baidu.com
反向代理
server {
listen 8080;
# 用户访问 ip:8080/test 下的所有路径代理到 github
location /test {
proxy_pass https://github.com;
}
# 所有 /api 下的接口访问都代理到本地的 8888 端口
# 例如你本地运行的 java 服务的端口是 8888,接口都是以 /api 开头
location /api {
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8888;
}
}
反向代理还有一些其他的指令,可以了解一下:
proxy_set_header:在将客户端请求发送给后端服务器之前,更改来自客户端的请求头信息。
proxy_connect_timeout:配置Nginx与后端代理服务器尝试建立连接的超时时间。
proxy_read_timeout:配置Nginx向后端服务器组发出read请求后,等待相应的超时时间。
proxy_send_timeout:配置Nginx向后端服务器组发出write请求后,等待相应的超时时间。
proxy_redirect:用于修改后端服务器返回的响应头中的Location和Refresh。
访问控制
server {
location ~ ^/index.html {
# 匹配 index.html 页面 除了 127.0.0.1 以外都可以访问
deny 192.168.1.1;
deny 192.168.1.2;
allow all;
}
}
上面的命令表示禁止 192.168.1.1 和 192.168.1.2 两个 ip 访问,其它全部允许。从上到下的顺序,匹配到了便跳出,可以按你的需求设置。
负载均衡
通过负载均衡充利用服务器资源,nginx 目前支持自带 4 种负载均衡策略,还有 2 种常用的第三方策略。
轮询策略(默认)
每个请求按时间顺序逐一分配到不同的后端服务器,如果有后端服务器挂掉,能自动剔除。但是如果其中某一台服务器压力太大,出现延迟,会影响所有分配在这台服务器下的用户。
http {
upstream test.com {
server 192.168.1.12:8887;
server 192.168.1.13:8888;
}
server {
location /api {
proxy_pass http://test.com;
}
}
}
根据服务器权重
例如要配置:10 次请求中大概 1 次访问到 8888 端口,9 次访问到 8887 端口:
http {
upstream test.com {
server 192.168.1.12:8887 weight=9;
server 192.168.1.13:8888 weight=1;
}
server {
location /api {
proxy_pass http://test.com;
}
}
}
客户端 ip 绑定(ip_hash)
来自同一个 ip 的请求永远只分配一台服务器,有效解决了动态网页存在的 session 共享问题。例如:比如把登录信息保存到了 session 中,那么跳转到另外一台服务器的时候就需要重新登录了。
所以很多时候我们需要一个客户只访问一个服务器,那么就需要用 ip_hash 了。
http {
upstream test.com {
ip_hash;
server 192.168.1.12:8887;
server 192.168.1.13:8888;
}
server {
location /api {
proxy_pass http://test.com;
}
}
}
最小连接数策略
将请求优先分配给压力较小的服务器,它可以平衡每个队列的长度,并避免向压力大的服务器添加更多的请求。
http {
upstream test.com {
least_conn;
server 192.168.1.12:8887;
server 192.168.1.13:8888;
}
server {
location /api {
proxy_pass http://test.com;
}
}
}
最快响应时间策略(依赖于第三方 NGINX Plus)
依赖于 NGINX Plus,优先分配给响应时间最短的服务器。
http {
upstream test.com {
fair;
server 192.168.1.12:8887;
server 192.168.1.13:8888;
}
server {
location /api {
proxy_pass http://test.com;
}
}
}
按访问 url 的 hash 结果(第三方)
按访问 url 的 hash 结果来分配请求,使每个 url 定向到同一个后端服务器,后端服务器为缓存时比较有效。在 upstream 中加入 hash 语句,server 语句中不能写入 weight 等其他的参数,hash_method 是使用的 hash 算法
http {
upstream test.com {
hash $request_uri;
hash_method crc32;
server 192.168.1.12:8887;
server 192.168.1.13:8888;
}
server {
location /api {
proxy_pass http://test.com;
}
}
}
采用 HAproxy 的 loadbalance uri 或者 nginx 的 upstream_hash 模块,都可以做到针对 url 进行哈希算法式的负载均衡转发。
配置图片、字体等静态文件缓存
由于图片、字体、音频、视频等静态文件在打包的时候通常会增加了 hash,所以缓存可以设置的长一点,先设置强制缓存,再设置协商缓存;如果存在没有 hash 值的静态文件,建议不设置强制缓存,仅通过协商缓存判断是否需要使用缓存。
# 图片缓存时间设置
location ~ .*\.(css|js|jpg|png|gif|swf|woff|woff2|eot|svg|ttf|otf|mp3|m4a|aac|txt)$ {
expires 10d;
}
# 如果不希望缓存过期
expires -1;
gzip 压缩
开启 gzip 压缩可以大幅减少 http 传输过程中文件的大小,可以极大的提高网站的访问速度,基本是必不可少的优化操作:
gzip on; # 开启gzip 压缩
# gzip_types
# gzip_static on;
# gzip_proxied expired no-cache no-store private auth;
# gzip_buffers 16 8k;
gzip_min_length 1k;
gzip_comp_level 4;
gzip_http_version 1.0;
gzip_vary off;
gzip_disable "MSIE [1-6]\.";
解释一下:
- gzip_types:要采用 gzip 压缩的 MIME 文件类型,其中 text/html 被系统强制启用;
- gzip_static:默认 off,该模块启用后,Nginx 首先检查是否存在请求静态文件的 gz 结尾的文件,如果有则直接返回该 .gz 文件内容;
- gzip_proxied:默认 off,nginx 做为反向代理时启用,用于设置启用或禁用从代理服务器上收到相应内容 gzip 压缩;
- gzip_buffers:获取多少内存用于缓存压缩结果,16 8k 表示以 8k*16 为单位获得;
- gzip_min_length:允许压缩的页面最小字节数,页面字节数从 header 头中的 Content-Length 中进行获取。默认值是 0,不管页面多大都压缩。建议设置成大于 1k 的字节数,小于 1k 可能会越压越大;
- gzip_comp_level:gzip 压缩比,压缩级别是 1-9,1 压缩级别最低,9 最高,级别越高压缩率越大,压缩时间越长,建议 4-6;
- gzip_http_version:默认 1.1,启用 gzip 所需的 HTTP 最低版本;
- gzip_vary:用于在响应消息头中添加 Vary:Accept-Encoding,使代理服务器根据请求头中的 Accept-Encoding 识别是否启用 gzip 压缩;
- gzip_disable 指定哪些不需要 gzip 压缩的浏览器
其中第 2 点,普遍是结合前端打包的时候打包成 gzip 文件后部署到服务器上,这样服务器就可以直接使用 gzip 的文件了,并且可以把压缩比例提高,这样 nginx 就不用压缩,也就不会影响速度。一般不追求极致的情况下,前端不用做任何配置就可以使用啦~
HTTP 服务器
nginx 本身也是一个静态资源的服务器,当只有静态资源的时候,就可以使用 nginx 来做服务器:
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location / {
root /usr/local/app;
index index.html;
}
}
这样如果访问 http://ip 就会默认访问到 /usr/local/app 目录下面的 index.html,如果一个网站只是静态页面的话,那么就可以通过这种方式来实现部署,比如一个静态官网。
动静分离
就是把动态和静态的请求分开。方式主要有两种:
- 一种是纯粹把静态文件独立成单独的域名,放在独立的服务器上,也是目前主流推崇的方案
- 一种方法就是动态跟静态文件混合在一起发布, 通过 nginx 配置来分开
# 所有静态请求都由nginx处理,存放目录为 html
location ~ \.(gif|jpg|jpeg|png|bmp|swf|css|js) {
root /usr/local/resource;
expires 10h; # 设置过期时间为10小时
}
# 所有动态请求都转发给 tomcat 处理
location ~ \.(jsp|do) {
proxy_pass 127.0.0.1:8888;
}
注意上面设置了 expires,当 nginx 设置了 expires 后,例如设置为:expires 10d; 那么,所在的 location 或 if 的内容,用户在 10 天内请求的时候,都只会访问浏览器中的缓存,而不会去请求 nginx 。
请求限制
对于大流量恶意的访问,会造成带宽的浪费,给服务器增加压力。可以通过 nginx 对于同一 IP 的连接数以及并发数进行限制。合理的控制还可以用来防止 DDos 和 CC 攻击。
关于请求限制主要使用 nginx 默认集成的 2 个模块:
- limit_conn_module 连接频率限制模块
- limit_req_module 请求频率限制模块
涉及到的配置主要是:
- limit_req_zone 限制请求数
- limit_conn_zone 限制并发连接数
通过 limit_conn_zone 限制并发连接数
http{
limit_conn_zone $binary_remote_addrzone=limit:10m; // 设置共享内存空间大
server{
location /{
limit_conn addr 5; # 同一用户地址同一时间只允许有5个连接。
}
}
}
如果共享内存空间被耗尽,服务器将会对后续所有的请求返回 503 (Service Temporarily Unavailable) 错误。
当多个 limit_conn_zone 指令被配置时,所有的连接数限制都会生效。比如,下面配置不仅会限制单一 IP 来源的连接数,同时也会限制单一虚拟服务器的总连接数:
limit_conn_zone binary_remote_addr zone=perip:10m;
limit_conn_zone server_name zone=perserver:10m;
server {
limit_conn perip 10; # 限制每个 ip 连接到服务器的数量
limit_conn perserver 2000; # 限制连接到服务器的总数
}
通过 limit_req_zone 限制请求数
limit_req_zone $binary_remote_addr zone=creq:10 mrate=10r/s;
server{
location /{
limit_req zone=creq burst=5;
}
}
限制平均每秒不超过一个请求,同时允许超过频率限制的请求数不多于 5 个。如果不希望超过的请求被延迟,可以用 nodelay 参数,如:
limit_req zone=creq burst=5 nodelay;
正向代理
正向代理,意思是一个位于客户端和原始服务器(origin server)之间的服务器,为了从原始服务器取得内容,客户端向代理发送一个请求并指定目标(原始服务器),然后代理向原始服务器转交请求并将获得的内容返回给客户端。客户端才能使用正向代理,比如我们使用的 VPN 服务就是正向代理,直观区别:
配置正向代理:
resolver 8.8.8.8 # 谷歌的域名解析地址
server {
resolver_timeout 5s; // 设超时时间
location / {
# 当客户端请求我的时候,我会把请求转发给它
# host 要访问的主机名 request_uri 请求路径
proxy_pass http://hostrequest_uri;
}
}
正向代理的对象是客户端,服务器端看不到真正的客户端。
图片防盗链
server {
listen 80;
server_name *.test;
# 图片防盗链
location ~* \.(gif|jpg|jpeg|png|bmp|swf) {
valid_referers none blocked server_names ~\.google\. ~\.baidu\. *.qq.com; # 只允许本机 IP 外链引用,将百度和谷歌也加入白名单有利于 SEO
if (invalid_referer){
return 403;
}
}
}
以上设置就能防止其它网站利用外链访问我们的图片,有利于节省流量
适配 PC 或移动设备
根据用户设备不同返回不同样式的站点,以前经常使用的是纯前端的自适应布局,但是复杂的网站并不适合响应式,无论是复杂性和易用性上面还是不如分开编写的好,比如我们常见的淘宝、京东。
根据用户请求的 user-agent 来判断是返回 PC 还是 H5 站点:
server {
listen 80;
server_name test.com;
location / {
root /usr/local/app/pc; # pc 的 html 路径
if ($http_user_agent ~* '(Android|webOS|iPhone|iPod|BlackBerry)') {
root /usr/local/app/mobile; # mobile 的 html 路径
}
index index.html;
}
}
设置二级域名
新建一个 server 即可:
server {
listen 80;
server_name admin.test.com; // 二级域名
location / {
root /usr/local/app/admin; # 二级域名的 html 路径
index index.html;
}
}
配置 HTTPS
修改 nginx 配置:
server {
listen 443 ssl http2 default_server; # SSL 访问端口号为 443
server_name sherlocked93.club; # 填写绑定证书的域名
ssl_certificate /etc/nginx/https/1_sherlocked93.club_bundle.crt; # 证书文件地址
ssl_certificate_key /etc/nginx/https/2_sherlocked93.club.key; # 私钥文件地址
ssl_session_timeout 10m;
ssl_protocols TLSv1 TLSv1.1 TLSv1.2; #请按照以下协议配置
ssl_ciphers ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5:!RC4:!DHE;
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
location / {
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
}
写完 nginx -t -q 校验一下,没问题就 nginx -s reload,现在去访问 https://sherlocked93.club/ 就能访问 HTTPS 版的网站了。
一般还可以加上几个增强安全性的命令:
add_header X-Frame-Options DENY; # 减少点击劫持
add_header X-Content-Type-Options nosniff; # 禁止服务器自动解析资源类型
add_header X-Xss-Protection 1; # 防XSS攻击
配置 HTTP 转 HTTPS
server {
listen 80;
server_name test.com www.test.com;
# 单域名重定向
if (host = 'www.sherlocked93.club'){
return 301 https://www.sherlocked93.clubrequest_uri;
}
# 全局非 https 协议时重定向
if (scheme != 'https') {
return 301 https://server_namerequest_uri;
}
# 或者全部重定向
return 301 https://server_name$request_uri;
}
以上配置选择自己需要的一条即可,不用全部加。
单页面项目 history 路由配置
server {
listen 80;
server_name fe.sherlocked93.club;
location / {
root /usr/local/app/dist; # vue 打包后的文件夹
index index.html index.htm;
try_files uri uri/ /index.html @rewrites; # 默认目录下的 index.html,如果都不存在则重定向
expires -1; # 首页一般没有强制缓存
add_header Cache-Control no-cache;
}
location @rewrites { // 重定向设置
rewrite ^(.+)$ /index.html break;
}
}
配置高可用集群(双机热备)
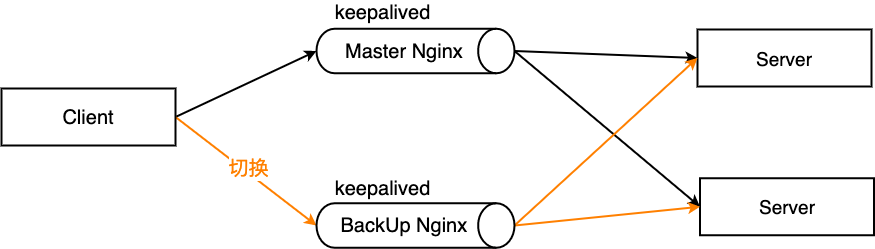
当主 nginx 服务器宕机之后,切换到备份的 nginx 服务器
首先安装 keepalived:
yum install keepalived -y
然后编辑 /etc/keepalived/keepalived.conf 配置文件,并在配置文件中增加 vrrp_script 定义一个外围检测机制,并在 vrrp_instance 中通过定义 track_script 来追踪脚本执行过程,实现节点转移:
global_defs{
notification_email {
cchroot@gmail.com
}
notification_email_from test@firewall.loc
smtp_server 127.0.0.1
smtp_connect_timeout 30 // 上面都是邮件配置
router_id LVS_DEVEL // 当前服务器名字,用 hostname 命令来查看
}
vrrp_script chk_maintainace { // 检测机制的脚本名称为chk_maintainace
script "[[ -e/etc/keepalived/down ]] && exit 1 || exit 0" // 可以是脚本路径或脚本命令
// script "/etc/keepalived/nginx_check.sh" // 比如这样的脚本路径
interval 2 // 每隔2秒检测一次
weight -20 // 当脚本执行成立,那么把当前服务器优先级改为-20
}
vrrp_instanceVI_1 { // 每一个vrrp_instance就是定义一个虚拟路由器
state MASTER // 主机为MASTER,备用机为BACKUP
interface eth0 // 网卡名字,可以从ifconfig中查找
virtual_router_id 51 // 虚拟路由的id号,一般小于255,主备机id需要一样
priority 100 // 优先级,master的优先级比backup的大
advert_int 1 // 默认心跳间隔
authentication { // 认证机制
auth_type PASS
auth_pass 1111 // 密码
}
virtual_ipaddress { // 虚拟地址vip
172.16.2.8
}
}
其中检测脚本 nginx_check.sh ,这里提供一个:
#!/bin/bash
A=`ps -C nginx --no-header | wc -l`
if [ $A -eq 0 ];then
/usr/sbin/nginx # 尝试重新启动nginx
sleep 2 # 睡眠2秒
if [ `ps -C nginx --no-header | wc -l` -eq 0 ];then
killall keepalived # 启动失败,将keepalived服务杀死。将vip漂移到其它备份节点
fi
fi
复制一份到备份服务器,备份 nginx 的配置要
- 将 state 后改为 BACKUP
- 将 priority 改为比主机小。设置完毕后各自
设置完毕后各自 service keepalived start 启动,经过访问成功之后,可以把 Master 机的 keepalived 停掉,此时 Master 机就不再是主机了 service keepalived stop,看访问虚拟 IP 时是否能够自动切换到备机 ip addr。
再次启动 Master 的 keepalived,此时 vip 又变到了主机上。
代理缓存
nginx 的 http_proxy 模块,提供类似于 Squid 的缓存功能,使用 proxy_cache_path 来配置。
nginx 可以对访问过的内容在 nginx 服务器本地建立副本,这样在一段时间内再次访问该数据,就不需要通过 nginx 服务器再次向后端服务器发出请求,减小数据传输延迟,提高访问速度:
proxy_cache_path usr/local/cache levels=1:2 keys_zone=my_cache:10m;
server {
listen 80;
server_name test.com;
location / {
proxy_cache my_cache;
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8888;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
}
}
上面的配置表示:nginx 提供一块 10 M 的内存用于缓存,名字为 my_cache, levels 等级为 1:2,缓存存放的路径为 usr/local/cache
访问日志
访问日志默认是注释的状态,需要可以打开和进行更详细的配置,一下是 nginx 的默认配置:
http {
log_format main 'remote_addr - remote_user [time_local] "request" '
'status body_bytes_sent "http_referer" '
'"http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
access_log logs/access.log main;
}
错误日志
错误日志放在 main 全局区块中,童鞋们打开 nginx.conf 就可以看见在配置文件中和下面一样的代码了:
#error_log logs/error.log;
#error_log logs/error.log notice;
#error_log logs/error.log info;
nginx 错误日志默认配置为:
error_log logs/error.log error;
静态资源服务器
server {
listen 80;
server_name static.bin;
charset utf-8; # 防止中文文件名乱码
location /download {
alias /usr/share/nginx/static; # 静态资源目录
autoindex on; # 开启静态资源列目录,浏览目录权限
autoindex_exact_size off; # on(默认)显示文件的确切大小,单位是byte;off显示文件大概大小,单位KB、MB、GB
autoindex_localtime off; # off(默认)时显示的文件时间为GMT时间;on显示的文件时间为服务器时间
}
}
禁止指定 user_agent
nginx 可以禁止指定的浏览器和爬虫框架访问:
# http_user_agent 为浏览器标识
# 禁止 user_agent 为baidu、360和sohu,~*表示不区分大小写匹配
if (http_user_agent ~* 'baidu|360|sohu') {
return 404;
}
# 禁止 Scrapy 等工具的抓取
if (http_user_agent ~* (Scrapy|Curl|HttpClient)) {
return 403;
`
#### 请求过滤
**根据请求类型过滤**
`# 非指定请求全返回 403
if ( request_method !~ ^(GET|POST|HEAD) ) {
return 403;
}
根据状态码过滤
error_page 502 503 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
}
这样实际上是一个内部跳转,当访问出现 502、503 的时候就能返回 50x.html 中的内容,这里需要注意是否可以找到 50x.html 页面,所以加了个 location 保证找到你自定义的 50x 页面。
根据 URL 名称过滤
if (host = zy.com' ) {
#其中 1是取自regex部分()里的内容,匹配成功后跳转到的URL。
rewrite ^/(.*) http://www.zy.com/1 permanent;
}
location /test {
// /test 全部重定向到首页
rewrite ^(.*)$ /index.html redirect;
}
ab 命令
ab 命令全称为:Apache bench,是 Apache 自带的压力测试工具,也可以测试 Nginx、IIS 等其他 Web 服务器:
- -n 总共的请求数
- -c 并发的请求数
- -t 测试所进行的最大秒数,默认值 为 50000
- -p 包含了需要的 POST 的数据文件
- -T POST 数据所使用的 Content-type 头信息
ab -n 1000 -c 5000 http://127.0.0.1/ # 每次发送1000并发的请求数,请求数总数为5000。
测试前需要安装 httpd-tools:
yum install httpd-tools
泛域名路径分离
这是一个非常实用的技能,经常有时候我们可能需要配置一些二级或者三级域名,希望通过 nginx 自动指向对应目录,比如:
- test1.doc.test.club 自动指向 /usr/local/html/doc/test1 服务器地址;
- test2.doc.test.club 自动指向 /usr/local/html/doc/test2 服务器地
址;
server {
listen 80;
server_name ~^([\w-]+)\.doc\.test\.club;
root /usr/local/html/doc/1;
}
泛域名转发
和之前的功能类似,有时候我们希望把二级或者三级域名链接重写到我们希望的路径,让后端就可以根据路由解析不同的规则:
test1.serv.test.club/api\?name=a 自动转发到 127.0.0.1:8080/test1/api\?name=a
test2.serv.test.club/api\?name=a 自动转发到 127.0.0.1:8080/test2/api\?name=a
配置
server {
listen 80;
server_name ~^([\w-]+)\.serv\.test\.club;
location / {
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header Host http_host;
proxy_set_header X-NginX-Proxy true;
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8080/1request_uri;
}
}
nginx升级与回退
1、先确认旧的nginx进程是已经存在的
旧版本nginx启动进程
[root@master2 nginx]# ps aux | grep nginx
root 17440 0.0 0.0 79732 1496 ? Ss 11:42 0:00 nginx: master process sbin/nginx
nobody 17441 0.0 0.0 80120 2212 ? S 11:42 0:00 nginx: worker process
nobody 17442 0.0 0.1 80120 2456 ? S 11:42 0:00 nginx: worker process
nobody 17443 0.0 0.0 80120 2212 ? S 11:42 0:00 nginx: worker process
nobody 17444 0.0 0.1 80120 2456 ? S 11:42 0:00 nginx: worker process
nobody 17445 0.0 0.0 80120 2212 ? S 11:42 0:00 nginx: worker process
旧版本的nginx我已经启动了,设置5个worker进程。
2、开始编译安装新版本1.18.0的nginx
wget http://nginx.org/download/nginx-1.18.0.tar.gz
mv nginx-1.18.0.tar.gz /usr/local
cd /usr/local
tar xf nginx-1.18.0.tar.gz
先获取旧版本nginx编译的选项
[root@master2 nginx]# sbin/nginx -V
nginx version: nginx/1.16.1
built by gcc 4.8.5 20150623 (Red Hat 4.8.5-39) (GCC)
built with OpenSSL 1.0.2k-fips 26 Jan 2017
TLS SNI support enabled
configure arguments: --prefix=/usr/local/nginx --with-http_ssl_module --with-http_v2_module --with-http_realip_module --with-http_addition_module --with-http_image_filter_module --with-http_geoip_module --with-http_gunzip_module --with-http_stub_status_module --with-http_gzip_static_module --with-pcre --with-stream --with-stream_ssl_module --with-stream_realip_module
拿到这个选项,然后放在新版本nginx里面。执行configure
[root@master2 nginx-1.18.0]# pwd
/usr/local/nginx-1.18.0
[root@master2 nginx-1.18.0]# ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx --with-http_ssl_module --with-http_v2_module --with-http_realip_module --with-http_addition_module --with-http_image_filter_module --with-http_geoip_module --with-http_gunzip_module --with-http_stub_status_module --with-http_gzip_static_module --with-pcre --with-stream --with-stream_ssl_module --with-stream_realip_module
checking for GeoIP IPv6 support ... found
creating objs/Makefile
Configuration summary
+ using system PCRE library
+ using system OpenSSL library
+ using system zlib library
nginx path prefix: "/usr/local/nginx"
nginx binary file: "/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx"
nginx modules path: "/usr/local/nginx/modules"
nginx configuration prefix: "/usr/local/nginx/conf"
nginx configuration file: "/usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf"
nginx pid file: "/usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid"
nginx error log file: "/usr/local/nginx/logs/error.log"
nginx http access log file: "/usr/local/nginx/logs/access.log"
nginx http client request body temporary files: "client_body_temp"
nginx http proxy temporary files: "proxy_temp"
nginx http fastcgi temporary files: "fastcgi_temp"
nginx http uwsgi temporary files: "uwsgi_temp"
nginx http scgi temporary files: "scgi_temp"
注意:有些人可能有疑惑,新下载的nginx在执行./configure的时候–prefix指定的目录是需要指向旧的nginx所指向的prefix目录还是随便指向一个就行,答案是需要指向旧版本的nginx的安装目录
执行make命令
[root@master2 nginx-1.18.0]# make && make install
3、平滑升级
3.1、先备份旧的nginx二进制可执行程序
[root@master2 nginx-1.18.0]# cd /usr/local/nginx/sbin
[root@master2 sbin]# ls
nginx
[root@master2 sbin]# cp nginx{,.bak}
[root@master2 sbin]# ls
nginx nginx.bak
3.2、查看未升级前的nginx版本
[root@master2 sbin]# ./nginx -V
nginx version: nginx/1.16.1
built by gcc 4.8.5 20150623 (Red Hat 4.8.5-39) (GCC
xxxx
xxx
3.3、找到nginx-1.18.0新版本的nginx的二进制执行程序
[root@master2 sbin]# cd /usr/local/nginx-1.18.0/
[root@master2 nginx-1.18.0]# ls
auto CHANGES CHANGES.ru conf configure contrib html LICENSE Makefile man objs README src
[root@master2 nginx-1.18.0]# cd objs
[root@master2 objs]# ls
autoconf.err Makefile nginx nginx.8 ngx_auto_config.h ngx_auto_headers.h ngx_modules.c ngx_modules.o src
上面的这个 nginx 就是我们要拿到的新版本的nginx可执行程序文件。
3.4、使用nginx-1.18.0的二进制文件将nginx-1.16.1的二进制文件进行强制覆盖
[root@master2 objs]# cp -f nginx /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
cp: overwrite ‘/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx’? y
3.5、设定旧的服务不再接收用户请求(下线),新服务启动子进程接收用户请求(上线)
先查看当前未升级的nginx进程(这是旧版本的nginx进程)
[root@master2 objs]# ps aux | grep nginx
root 17440 0.0 0.0 79732 1496 ? Ss 11:42 0:00 nginx: master process sbin/nginx
nobody 17441 0.0 0.0 80120 2212 ? S 11:42 0:00 nginx: worker process
nobody 17442 0.0 0.1 80120 2456 ? S 11:42 0:00 nginx: worker process
nobody 17443 0.0 0.0 80120 2212 ? S 11:42 0:00 nginx: worker process
nobody 17444 0.0 0.1 80120 2456 ? S 11:42 0:00 nginx: worker process
nobody 17445 0.0 0.1 80120 2456 ? S 11:42 0:00 nginx: worker process
找到nginx父进程的pid号,现在对其发送 USR2 信号
[root@master2 objs]# kill -USR2 17440 #设定新的子进程开始接收用户的访问请求,旧的不再接受用户的访问请求
再次查看进程
[root@master2 objs]# ps aux | grep nginx
root 17440 0.0 0.0 79732 1496 ? Ss 11:42 0:00 nginx: master process sbin/nginx
nobody 17441 0.0 0.0 80120 2212 ? S 11:42 0:00 nginx: worker process
nobody 17442 0.0 0.1 80120 2456 ? S 11:42 0:00 nginx: worker process
nobody 17443 0.0 0.0 80120 2212 ? S 11:42 0:00 nginx: worker process
nobody 17444 0.0 0.1 80120 2456 ? S 11:42 0:00 nginx: worker process
nobody 17445 0.0 0.1 80120 2456 ? S 11:42 0:00 nginx: worker process
root 21081 0.5 0.1 79740 4080 ? S 20:00 0:00 nginx: master process sbin/nginx
nobody 21082 0.0 0.0 80192 2200 ? S 20:00 0:00 nginx: worker process
nobody 21083 0.0 0.0 80192 2200 ? S 20:00 0:00 nginx: worker process
nobody 21084 0.0 0.0 80192 2200 ? S 20:00 0:00 nginx: worker process
nobody 21085 0.0 0.0 80192 2200 ? S 20:00 0:00 nginx: worker process
nobody 21086 0.0 0.0 80192 2200 ? S 20:00 0:00 nginx: worker process
现在是nginx的新老版本的进程共存的一种情况。虽然现在旧版本的nginx进程还存在,但是已经不再接受用户的请求了。除此之外,旧版本的nginx进程也依然处于监听的状态,我们通过lsof命令可以看到,比如:
[root@master2 objs]# lsof -p 17440 | grep LISTEN # 这里的pid号是旧版本的nginx的master进程的pid号
nginx 17440 root 6u IPv4 120768 0t0 TCP *:http (LISTEN)
虽然在监听,但实际不会处理新连接,因为fd已经从epoll中移出了。另外,旧master是新master的父进程,所以新master才能共享打开的监听端口。保留旧版本的master是为了方便回滚(当然你可以发信号QUIT或者直接杀掉进程)
3.6、进行旧服务进程的关闭
[root@master2 objs]# kill -WINCH 17440 # 进行旧服务进程的关闭,该pid号是旧版本的nginx的master进程的pid号
再次查看当前nginx进程
[root@master2 objs]# ps aux | grep nginx
root 17440 0.0 0.0 79732 1652 ? Ss 11:42 0:00 nginx: master process sbin/nginx
root 21081 0.0 0.1 79740 4080 ? S 20:00 0:00 nginx: master process sbin/nginx
nobody 21082 0.0 0.0 80192 2200 ? S 20:00 0:00 nginx: worker process
nobody 21083 0.0 0.0 80192 2200 ? S 20:00 0:00 nginx: worker process
nobody 21084 0.0 0.0 80192 2200 ? S 20:00 0:00 nginx: worker process
nobody 21085 0.0 0.0 80192 2200 ? S 20:00 0:00 nginx: worker process
nobody 21086 0.0 0.0 80192 2200 ? S 20:00 0:00 nginx: worker process
可以看到现在的旧版本的nginx的worker进程已经全部被杀死了,只剩下的旧版本nginx的master进程
确定升级没有任何问题的话,那么现在我们可以把这个master进程给杀死掉。可以用kill -QUIT把旧master进程杀掉。方法已经教给大家了,但是这里我先不杀死,因为我还要往下演示如何回退。
3.7、查看当前nginx的版本
[root@master2 nginx]# sbin/nginx -V
nginx version: nginx/1.18.0
built by gcc 4.8.5 20150623 (Red Hat 4.8.5-39) (GCC)
built with OpenSSL 1.0.2k-fips 26 Jan 2017
TLS SNI support enabled
configure arguments: --prefix=/usr/local/nginx --with-http_ssl_module --with-http_v2_module --with-http_realip_module --with-http_addition_module --with-http_image_filter_module --with-http_geoip_module --with-http_gunzip_module --with-http_stub_status_module --with-http_gzip_static_module --with-pcre --with-stream --with-stream_ssl_module --with-stream_realip_module
可以看到现在已经升级成功了。还可以访问一下
4、现在我们演示一下如何回退
这种情况主要是用于当新版本的nginx升级失败之后,我们立马回退到旧版本的nginx
4.1、将旧版本的nginx二进制文件强行覆盖
[root@master2 sbin]# mv nginx.bak nginx
mv: overwrite ‘nginx’? y
``
查看进程
```bash
[root@master2 sbin]# ps aux | grep nginx
root 17440 0.0 0.0 79732 1652 ? Ss Aug20 0:00 nginx: master process sbin/nginx
root 21081 0.0 0.1 79740 4080 ? S Aug20 0:00 nginx: master process sbin/nginx
nobody 21082 0.0 0.0 80192 2200 ? S Aug20 0:00 nginx: worker process
nobody 21083 0.0 0.1 80192 2452 ? S Aug20 0:00 nginx: worker process
nobody 21084 0.0 0.0 80192 2200 ? S Aug20 0:00 nginx: worker process
nobody 21085 0.0 0.0 80192 2200 ? S Aug20 0:00 nginx: worker process
nobody 41895 0.0 0.0 80192 2200 ? S 10:53 0:00 nginx: worker process
4.2、向旧版本nginx进程发送HUP信号
[root@master2 sbin]# kill -HUP 17440 #注意这是旧版本的nginx进程pid号
说明一下:这个命令就相当与reload指令的作用,把旧的nginx的worker进程拉起来,但是咱们并不是直接使用reload的方式来执行,而是发送HUP信号,它会在没有worker进程时启动worker进程,这点需要注意一下。
此时再次查看进程
[root@master2 sbin]# ps aux | grep nginx
root 17440 0.0 0.0 79732 1652 ? Ss Aug20 0:00 nginx: master process sbin/nginx
root 21081 0.0 0.1 79740 4080 ? S Aug20 0:00 nginx: master process sbin/nginx
nobody 21082 0.0 0.0 80192 2200 ? S Aug20 0:00 nginx: worker process
nobody 21083 0.0 0.1 80192 2452 ? S Aug20 0:00 nginx: worker process
nobody 21084 0.0 0.0 80192 2200 ? S Aug20 0:00 nginx: worker process
nobody 21085 0.0 0.0 80192 2200 ? S Aug20 0:00 nginx: worker process
nobody 41895 0.0 0.0 80192 2200 ? S 10:53 0:00 nginx: worker process
nobody 42070 0.0 0.0 80120 2208 ? S 15:42 0:00 nginx: worker process
nobody 42071 0.0 0.0 80120 2208 ? S 15:42 0:00 nginx: worker process
nobody 42072 0.0 0.0 80120 2208 ? S 15:42 0:00 nginx: worker process
nobody 42073 0.0 0.0 80120 2208 ? S 15:42 0:00 nginx: worker process
nobody 42074 0.0 0.0 80120 2208 ? S 15:42 0:00 nginx: worker process
发现多了很多worker进程,多出来的部分是旧版本的nginx进程。
4.3、让新版本的服务停止接收用户请求
[root@master2 sbin]# kill -USR2 21081
此时,接收用户请求的是旧版本的nginx进程。新版本的nginx进程不再接受用户请求
4.4、进行新版本服务进程的关闭
[root@master2 sbin]# kill -WINCH 21081
查看一下进程
[root@master2 sbin]# ps aux | grep nginx
root 17440 0.0 0.0 79732 1652 ? Ss Aug20 0:00 nginx: master process sbin/nginx
root 21081 0.0 0.1 79740 4080 ? S Aug20 0:00 nginx: master process sbin/nginx
nobody 42070 0.0 0.0 80120 2208 ? S 15:42 0:00 nginx: worker process
nobody 42071 0.0 0.0 80120 2208 ? S 15:42 0:00 nginx: worker process
nobody 42072 0.0 0.0 80120 2208 ? S 15:42 0:00 nginx: worker process
nobody 42073 0.0 0.0 80120 2208 ? S 15:42 0:00 nginx: worker process
nobody 42074 0.0 0.0 80120 2208 ? S 15:42 0:00 nginx: worker process
现在,旧版本已经回退成功了,我们可以把新版本的nginx的master进程发送QUIT进程将其退出。
4.5、kill掉新版本nginx进程
[root@master2 sbin]# kill -QUIT 21081
[root@master2 sbin]# ps aux | grep nginx
root 17440 0.0 0.0 79732 1652 ? Ss Aug20 0:00 nginx: master process sbin/nginx
nobody 42070 0.0 0.0 80120 2208 ? S 15:42 0:00 nginx: worker process
nobody 42071 0.0 0.0 80120 2208 ? S 15:42 0:00 nginx: worker process
nobody 42072 0.0 0.0 80120 2208 ? S 15:42 0:00 nginx: worker process
nobody 42073 0.0 0.0 80120 2208 ? S 15:42 0:00 nginx: worker process
nobody 42074 0.0 0.0 80120 2208 ? S 15:42 0:00 nginx: worker process
现在已经回退成功了
最佳实践
- 为了使 Nginx 配置更易于维护,建议为每个服务创建一个单独的配置文件,存储在 /etc/nginx/conf.d 目录,根据需求可以创建任意多个独立的配置文件。
- 独立的配置文件,建议遵循以下命名约定 <服务>.conf,比如域名是 sherlocked93.club,那么你的配置文件的应该是这样的 /etc/nginx/conf.d/sherlocked93.club.conf,如果部署多个服务,也可以在文件名中加上 Nginx 转发的端口号,比如 sherlocked93.club.8080.conf,如果是二级域名,建议也都加上 fe.sherlocked93.club.conf。
- 常用的、复用频率比较高的配置可以放到 /etc/nginx/snippets 文件夹,在 Nginx 的配置文件中需要用到的位置 include 进去,以功能来命名,并在每个 snippet 配置文件的开头注释标明主要功能和引入位置,方便管理。比如之前的 gzip、cors 等常用配置,我都设置了 snippet。
- Nginx 日志相关目录,内以 域名.type.log 命名(比如 be.sherlocked93.club.access.log 和 be.sherlocked93.club.error.log )位于 /var/log/nginx/ 目录中,为每个独立的服务配置不同的访问权限和错误日志文件,这样查找错误时,会更加方便快捷。
Nginx 安全
ssl_dhparam
- 生成一个4096位的Diffie-Hellman参数文件,需要比较长的时间,看机器而定
openssl dhparam -out dhparam.pem 4096
2.在配置test.example.com.conf文件中增加以下内容:
listen 443 ssl;
ssl_certificate /home/howard/ssl/ssl.cer;
ssl_certificate_key /home/howard/ssl/ssl.key;
ssl_dhparam /home/howard/ssl/dhparam.pem;
ssl_protocols TLSv1 TLSv1.1 TLSv1.2;
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
ssl_ciphers "EECDH+ECDSA+AESGCM EECDH+aRSA+AESGCM EECDH+ECDSA+SHA384 EECDH+ECDSA+SHA256 EECDH+aRSA+SHA384 EECDH+aRSA+SHA256 EECDH+aRSA+RC4 EECDH EDH+aRSA RC4 !aNULL !eNULL !LOW !3DES !MD5 !EXP !PSK !SRP !DSS !MEDIUM";
add_header Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=63072000; includeSubDomains; preload";
add_header X-Frame-Options DENY;
add_header X-Content-Type-Options nosniff;
https 自签名SSL证书
创建SSL证书
sudo openssl req -x509 -nodes -days 365 -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout /etc/ssl/private/nginx-selfsigned.key -out /etc/ssl/certs/nginx-selfsigned.crt
您将被问到一系列问题。在我们讨论之前,让我们看看我们发出的命令中发生了什么:
- openssl:这是用于创建和管理OpenSSL证书,密钥和其他文件的基本命令行工具。
- req:此子命令指定我们要使用X.509证书签名请求(CSR)管理。“X.509”是SSL和TLS为其密钥和证书管理所遵循的公钥基础结构标准。我们想要创建一个新的X.509证书,所以我们使用这个子命令。
- -x509:通过告诉实用程序我们要创建自签名证书而不是生成证书签名请求(通常会发生)来进一步修改上一个子命令。
- -nodes:这告诉OpenSSL跳过用密码保护我们的证书的选项。当服务器启动时,我们需要Nginx能够在没有用户干预的情况下读取文件。密码短语会阻止这种情况发生,因为我们必须在每次重启后输入密码。
- -days 365:此选项设置证书被视为有效的时间长度。我们在这里设置了一年。
- -newkey rsa:2048:这指定我们要同时生成新证书和新密钥。我们没有创建在上一步中签署证书所需的密钥,因此我们需要将其与证书一起创建。该rsa:2048部分告诉它制作一个2048位长的RSA密钥。
- -keyout:这一行告诉OpenSSL在哪里放置我们正在创建的生成的私钥文件。
- -out:这告诉OpenSSL在哪里放置我们正在创建的证书。
最重要的一行是Common Name (e.g. server FQDN or YOUR name)那一行。您需要输入与服务器关联的域名,或者是您服务器的公共IP地址。
整个提示将如下所示:
OutputCountry Name (2 letter code) [AU]:US
State or Province Name (full name) [Some-State]:New York
Locality Name (eg, city) []:New York City
Organization Name (eg, company) [Internet Widgits Pty Ltd]:Bouncy Castles, Inc.
Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) []:Ministry of Water Slides
Common Name (e.g. server FQDN or YOUR name) []:server_IP_address
Email Address []:admin@your_domain.com
您创建的两个文件都将放在/etc/ssl目录的相应子目录中。
在我们使用OpenSSL的同时,我们还应该创建一个强大的Diffie-Hellman组,用于与客户协商Perfect Forward Secrecy。
我们可以通过输入以下内容来执行:
sudo openssl dhparam -out /etc/ssl/certs/dhparam.pem 2048
这可能需要几分钟,但一旦完成,您将拥有一个强大的DH组/etc/ssl/certs/dhparam.pem,我们可以在我们的配置中使用。
Nginx 服务器参数优化
内核参数优化
vi /etc/sysctl.conf
net.ipv4.tcp_keepalive_time = 300
net.ipv4.tcp_keepalive_intvl = 10
net.ipv4.tcp_keepalive_probes = 5
net.ipv4.tcp_tw_reuse = 1
net.ipv4.tcp_tw_recycle = 0
net.ipv4.tcp_timestamps = 1
net.ipv4.tcp_ecn = 0
net.ipv4.tcp_sack = 1
net.ipv4.tcp_dsack = 0
net.ipv4.tcp_fin_timeout = 3
net.ipv4.tcp_rmem = 4096 2097152 16777216
net.ipv4.tcp_wmem = 4096 2097152 16777216
net.ipv4.tcp_max_orphans = 3276800
net.ipv4.tcp_max_tw_buckets = 18000
net.ipv4.tcp_no_metrics_save = 1
net.ipv4.tcp_max_syn_backlog = 262144 # 用于指定半连接SYN队列长度
net.ipv4.tcp_synack_retries = 2
net.ipv4.tcp_syn_retries = 2
net.ipv4.tcp_syncookies = 1
net.ipv4.tcp_mem = 196608 2097152 3145728
net.ipv4.ip_local_port_range = 1024 65000
net.core.rmem_default = 16777216
net.core.wmem_default = 16777216
net.core.rmem_max = 16777216
net.core.wmem_max = 16777216
net.core.somaxconn = 262144 # somaxconn用于指定全连接ACCEPT队列长度
net.core.netdev_max_backlog = 300000
fs.file-max = 1280000 # 参考 内存大小(MB)/4 * 256 的公式得出来的。基本环境为 16G内存
net.unix.max_dgram_qlen = 10000
TCP连接队列长度
- tcp_max_syn_backlog用于指定半连接SYN队列长度,当新连接到来时,系统会检测半连接SYN队列,如果队列已满,则无法处理该SYN请求,并在 /proc/net/netstat中的 ListenOverflows和 ListenDrops中增加统计计数
- somaxconn 用于指定全连接ACCEPT队列长度,当该队列满了以后,客户端发送的ACK包将无法被正确处理,并返回错误"connection reset by peer"
Nginx则会记录一条error日志
"no live upstreams while connecting to upstreams"
如果出现以上错误,我们需要考虑增大这两项的配置。
异常丢包错误
TCP有一种行为,可以缓存每个连接最新的时间戳,后续请求中如果时间戳小于缓存的时间戳,即视为无效,相应的数据包会被丢弃。
推荐设置:
net.ipv4.tcp_tw_reuse = 1
net.ipv4.tcp_tw_recycle = 0
net.ipv4.tcp_timestamps = 1
文件句柄限制
vim /etc/security/limits.conf
root soft nofile 100001
root hard nofile 100002
file-max是内核可分配的最大文件数,nr_open是单个进程可分配的最大文件数,所以在我们使用ulimit或limits.conf来设置时,nr_open 要大于 hard 的值,否则会造成系统无法登录等一系列问题。
临时端口
由于Nginx用作代理,每个到上游Web服务的TCP连接都要占用一个临时端口,因此我们需要修改 ip_local_port_range参数
修改 /etc/sysctl.conf文件,添加如下内容:
net.ipv4.ip_local_port_range = 1024 65535
net.ipv4.ip_local_reserved_ports = 8080, 8081, 9000-9010
其中,参数 ip_local_reserved_ports用于指定保留端口,这是为了防止服务端口被占用而无法启动。
Nginx 参数优化
backlog 优化
server {
listen 80 backlog=2048;
}
该参数决定了listen监听队列的大小,也就是accept queue队列的大小。
在使用listen函数时,内核会根据传入的backlog参数与系统内参参数somaxcoon,取其中最小值作为backlog的值。
所以你之前配置的内核参数,对于nginx来说,默认情况下,不管你设置多大,这个队列都是511,并没有达到优化的效果
这个参数在内核中通常默认128,可以通过 /proc/sys/net/core/somaxconn查看,接着通过简单测试测试backlog值的选择。
首先是初始配置,内核是默认128,nginx默认511(这个在源码中可以查看),然后通过ss查看
ss -ltp| grep nginx
LISTEN 0 128 *:https
默认的backlog值都是511, 故这里也建议改为511。但是多个域名都设置这个值的时候就会出现以下的提示重复报错。
所以我的建议是,用 ab 压测的方法,持续调整测试,取一个适合你业务的最大backlog值,一定要以业务代码进行测试,而不是单纯的调大backlog。
工作进程
Nginx性能强大的一个重要原因在于它采用多进程非阻塞I/O模型,因此我们要妥善利用这一点:
- worker_processes 默认的Nginx只有一个master进程一个worker进程,我们需要对其进行修改,可以设置为指定的个数,也可以设置为 auto,即系统的CPU核数。更多的worker数量将导致进程间竞争cpu资源,从而带来不必要的上下文切换。因此这里我们将它设置为cpu的核数即可: worker_processes auto
- worker_connections 每个worker可以处理的并发连接数,默认值512不是很够用,我们适当将它增大: worker_connections 4096
- Nginx支持以下I/O复用方法处理连接:select、 poll、 kqueue、 epoll、 rtsig、 /dev/poll、 eventport。它们分别适用于不同的操作系统,其中 epoll是Linux系统上面效率最高的: use epoll
KeepAlive
为了避免从Nginx到Web服务频繁的建立、断开连接,我们可以启用从HTTP 1.1开始支持的KeepAlive长连接特性,它可以大幅减少CPU和网络开销,在我们的实战中也是对性能提高最大的一环。keepalive必须和 proxy_http_version与 proxy_set_header结合使用,
参考配置如下:
upstream BACKEND {
keepalive 300;
server 127.0.0.1:8081;
}
server {
listen 8080;
location / {
proxy_pass http://BACKEND;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Connection "";
}
}
其中 keepalive 既非 timeout,也不是连接池数量,它的意思是“最大空闲长连接数量”,超出这个数量的空闲长连接将被回收,当请求数量稳定而平滑时,空闲长连接数量将会非常小(接近于0),而现实中请求数量是不可能一直平滑而稳定的,当请求数量有波动时,空闲长连接数量也随之波动:
- 当空闲长连接数量大于配置值时,将会导致大于配置值的那部分长连接被回收;
- 当长连接不够用时,将会重新建立新的长连接。
因此,如果这个值过小的话,就会导致连接池频繁的回收、分配、再回收。
为了避免这种情况出现,可以根据实际情况适当调整这个值,在我们实际情况中,目标QPS为6000,Web服务响应时间约为200ms,因此需要约1200个长连接,而 keepalive值取长连接数量的10%~30%就可以了,这里我们取300,如果不想计算,直接设为1000也是可行的。
Access-Log缓存
记录日志的I/O开销比较高,好在Nginx支持日志缓存,我们可以利用这个功能,降低写日志文件的频率,从而提高性能。可以将 buffer和 flush两个参数结合使用来控制缓存行为:
access_log /var/logs/nginx-access.log buffer=64k gzip flush=1m
buffer制定了缓存大小,当缓冲区达到 buffer所指定的大小时,Nginx就会将缓存起来的日志写到文件中;
flush指定了缓存超时时间,当 flush指定的时间到达时,也会触发缓存日志写入文件操作。
文件描述符限制
上一节中已经对Linux系统的文件描述符限制进行了修改,Nginx配置中同样有相应的配置项:worker_rlimit_nofile, 理论上这个值应该设置为 /etc/security/limits.conf 中的值除以 worker_processes, 但实际中不可能每个进程均匀分配,所以这里只要设置成和 /etc/security/limits.conf 一样就可以了
worker_rlimit_nofile 1000000;
